Some of the top ransomware gangs are deploying a new pressure tactic to push more victim organizations into paying an extortion demand: Emailing the victim’s customers and partners directly, warning that their data will be leaked to the dark web unless they can convince the victim firm to pay up.
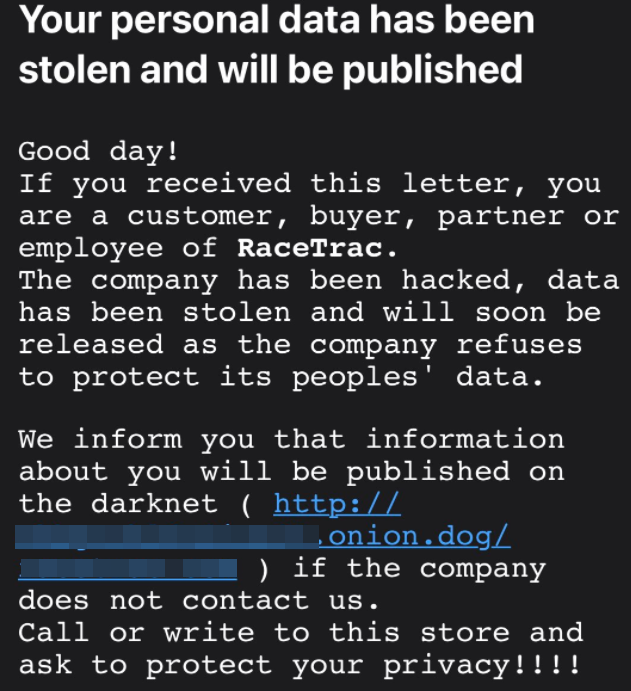
This letter is from the Clop ransomware gang, putting pressure on a recent victim named on Clop’s dark web shaming site.
“Good day! If you received this letter, you are a customer, buyer, partner or employee of [victim],” the missive reads. “The company has been hacked, data has been stolen and will soon be released as the company refuses to protect its peoples’ data.”
“We inform you that information about you will be published on the darknet [link to dark web victim shaming page] if the company does not contact us,” the message concludes. “Call or write to this store and ask to protect your privacy!!!!”
The message above was sent to a customer of RaceTrac Petroleum, an Atlanta company that operates more than 650 retail gasoline convenience stores in 12 southeastern states. The person who shared that screenshot above isn’t a distributor or partner of RaceTrac, but they said they are a RaceTrac rewards member, so the company definitely has their email address and other information.
Several gigabytes of the company’s files — including employee tax and financial records — have been posted to the victim shaming site for the Clop ransomware gang.
In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, RaceTrac said it was recently impacted by a security incident affecting one of its third-party service providers, Accellion Inc.
For the past few months, attackers have been exploiting a a zero-day vulnerability in Accellion File Transfer Appliance (FTA) software, a flaw that has been seized upon by Clop to break into dozens of other major companies like oil giant Shell and security firm Qualys.
“By exploiting a previously undetected software vulnerability, unauthorized parties were able to access a subset of RaceTrac data stored in the Accellion File Transfer Service, including email addresses and first names of some of our RaceTrac Rewards Loyalty users,” the company wrote. “This incident was limited to the aforementioned Accellion services and did not impact RaceTrac’s corporate network. The systems used for processing guest credit, debit and RaceTrac Rewards transactions were not impacted.”
The same extortion pressure email has been going out to people associated with the University of California, which was one of several large U.S. universities that got hit with Clop ransomware recently. Most of those university ransomware incidents appeared to be tied to attacks on attacks on the same Accellion vulnerability, and the company has acknowledged roughly a third of its customers on that appliance got compromised as a result.
Clop is one of several ransom gangs that will demand two ransoms: One for a digital key needed to unlock computers and data from file encryption, and a second to avoid having stolen data published or sold online. That means even victims who opt not to pay to get their files and servers back still have to decide whether to pay the second ransom to protect the privacy of their customers.
As I noted in Why Paying to Delete Stolen Data is Bonkers, leaving aside the notion that victims might have any real expectation the attackers will actually destroy the stolen data, new research suggests a fair number of victims who do pay up may see some or all of the stolen data published anyway.
The email in the screenshot above differs slightly from those covered last week by Bleeping Computer, which was the first to spot the new victim notification wrinkle. Those emails say that the recipient is being contacted as they are a customer of the store, and their personal data, including phone numbers, email addresses, and credit card information, will soon be published if the store does not pay a ransom, writes Lawrence Abrams.
“Perhaps you bought something there and left your personal data. Such as phone, email, address, credit card information and social security number,” the Clop gang states in the email.
Fabian Wosar, chief technology officer at computer security firm Emsisoft, said the direct appeals to victim customers is a natural extension of other advertising efforts by the ransomware gangs, which recently included using hacked Facebook accounts to post victim shaming advertisements.
Wosar said Clop isn’t the only ransomware gang emailing victim customers.
“Clop likes to do it and I think REvil started as well,” Wosar said.
Earlier this month, Bleeping Computer reported that the REvil ransomware operation was planning on launching crippling distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks against victims, or making VOIP calls to victims’ customers to apply further pressure.
“Sadly, regardless of whether a ransom is paid, consumers whose data has been stolen are still at risk as there is no way of knowing if ransomware gangs delete the data as they promise,” Abrams wrote.