If you created an online account to manage your tax records with the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS), those login credentials will cease to work later this year. The agency says that by the summer of 2022, the only way to log in to irs.gov will be through ID.me, an online identity verification service that requires applicants to submit copies of bills and identity documents, as well as a live video feed of their faces via a mobile device.

The IRS says it will require ID.me for all logins later this summer.
McLean, Va.-based ID.me was originally launched in 2010 with the goal of helping e-commerce sites validate the identities of customers who might be eligible for discounts at various retail establishments, such as veterans, teachers, students, nurses and first responders.
These days, ID.me is perhaps better known as the online identity verification service that many states now use to help staunch the loss of billions of dollars in unemployment insurance and pandemic assistance stolen each year by identity thieves. The privately-held company says it has approximately 64 million users, and gains roughly 145,000 new users each day.
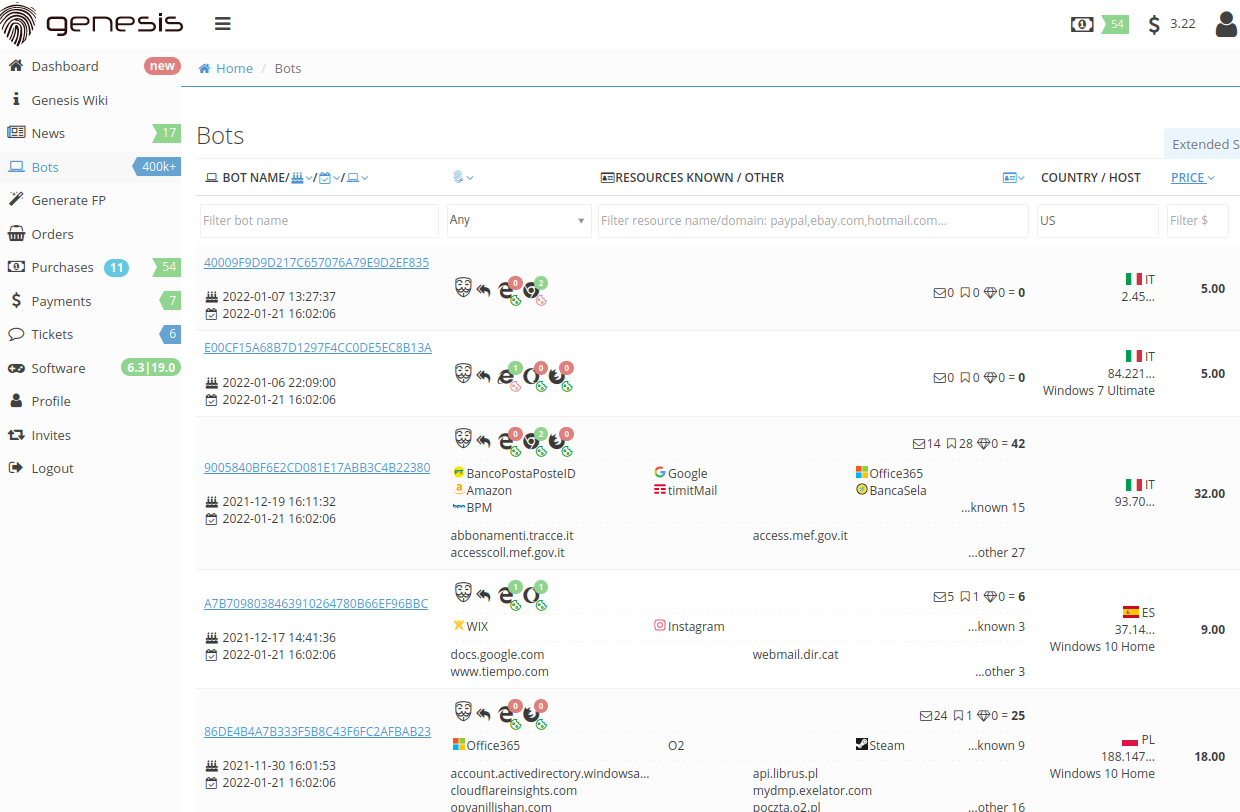
Some 27 states already use ID.me to screen for identity thieves applying for benefits in someone else’s name, and now the IRS is joining them. The service requires applicants to supply a great deal more information than typically requested for online verification schemes, such as scans of their driver’s license or other government-issued ID, copies of utility or insurance bills, and details about their mobile phone service.
When an applicant doesn’t have one or more of the above — or if something about their application triggers potential fraud flags — ID.me may require a recorded, live video chat with the person applying for benefits.
Since my credentials at the IRS will soon no longer work, I opted to create an ID.me account and share the experience here. An important preface to this walk-through is that verifying one’s self with Id.me requires one to be able to take a live, video selfie — either with the camera on a mobile device or a webcam attached to a computer (your webcam must be able to open on the device you’re using to apply for the ID.me account).
Also, successfully verifying your identity with ID.me may require a significant investment of time, and quite a bit of patience. For example, stepping away from one part of the many-step application process for a little more than five minutes necessitated another login, and then the re-submission of documents I’d previously uploaded.
 After entering an email address and picking a password, you are prompted to confirm your email address by clicking a link sent to that address. After confirmation, ID.me prompts users to choose a multi-factor authentication (MFA) option.
After entering an email address and picking a password, you are prompted to confirm your email address by clicking a link sent to that address. After confirmation, ID.me prompts users to choose a multi-factor authentication (MFA) option.
The MFA options range from a six-digit code sent via text message or phone call to code generator apps and FIDO Security Keys. ID.me even suggests using its own branded one-time code generating app, which can “push” a prompt to your mobile device for you to approve whenever you log in. I went with and would encourage others to use the strongest MFA option — a physical Security Key. For more on the benefits of using a Security Key for MFA, see this post.
When the MFA option is verified, the system produces a one-time backup code and suggests you save that in a safe place in case your chosen MFA option is unavailable the next time you try to use a service that requires ID.me.
Next, applicants are asked to upload images of their driver’s license, state-issued ID, or passport — either via a saved file or by scanning them with a webcam or mobile device.
If your documents get accepted, ID.me will then prompt you to take a live selfie with your mobile device or webcam. That took several attempts. When my computer’s camera produced an acceptable result, ID.me said it was comparing the output to the images on my driver’s license scans.
After this, ID.me requires the verification of your phone number, which means they will ask your mobile or landline provider to validate you are indeed an existing, paying customer who can be reached at that number. ID.me says it currently does not accept phone numbers tied to voice-over-IP services like Google Voice and Skype.
My application got stuck interminably at the “Confirming Your Phone” stage, which is somewhere near the middle of the entire verification process.
An email to ID.me’s support people generated a message with a link to complete the verification process via a live video chat. Unfortunately, clicking that link brought up prompts to re-upload all of the information I’d already supplied, and then some.
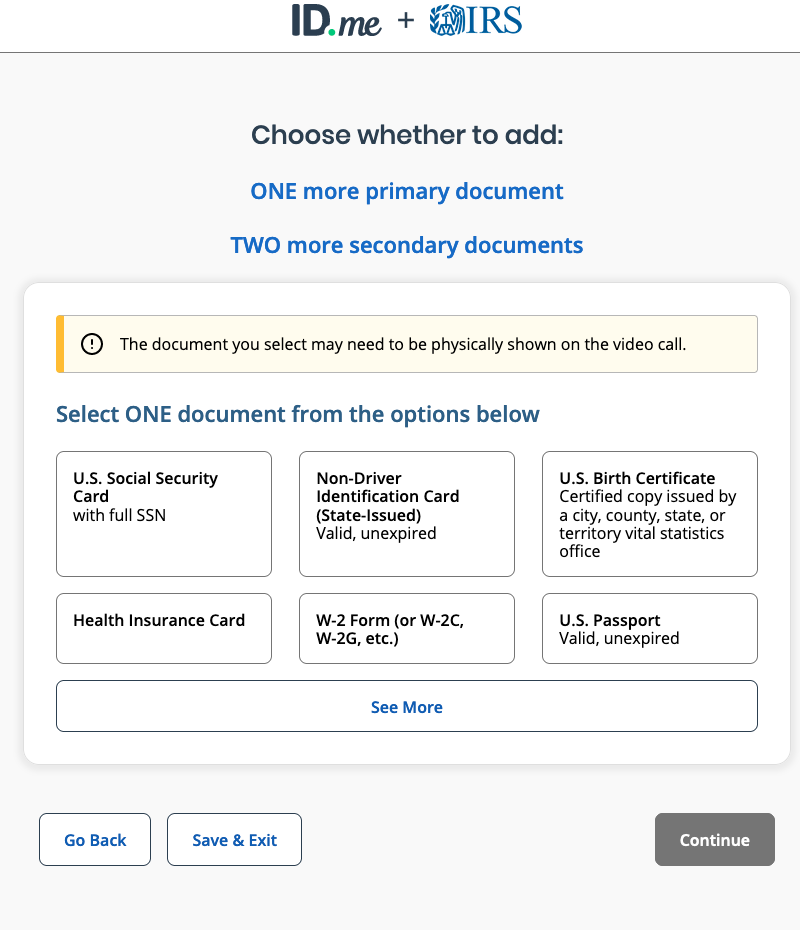
Some of the primary and secondary documents requested by ID.me.
For example, completing the process requires submitting at least two secondary identification documents, such as as a Social Security card, a birth certificate, health insurance card, W-2 form, electric bill, or financial institution statement.
After re-uploading all of this information, ID.me’s system prompted me to “Please stay on this screen to join video call.” However, the estimated wait time when that message first popped up said “3 hours and 27 minutes.”

I appreciate that ID.me’s system relies on real human beings seeking to interview applicants in real-time, and that not all of those representatives can be expected to handle all of these immediately. And I get that slowing things down is an important part of defeating identity fraudsters who are seeking to exploit automated identity verification systems that largely rely on static data about consumers.
That said, I started this “Meet an agent” process at around 9:30 in the evening, and I wasn’t particularly looking forward to staying up until midnight to complete it. But not long after the message about waiting 3 hours came up, I got a phone call from an ID.me technician who was CC’d on my original email to ID.me’s founder. Against my repeated protests that I wanted to wait my turn like everyone else, he said he would handle the process himself.
Sure enough, a minute later I was connected with the ID.me support person, who finished the verification in a video phone call. That took about one minute. But for anyone who fails the automated signup, count on spending several hours getting verified.
When my application was finally approved, I headed back to irs.gov and proceeded to log in with my new ID.me account. After granting the IRS access to the personal data I’d shared with ID.me, I was looking at my most recent tax data on the IRS website.
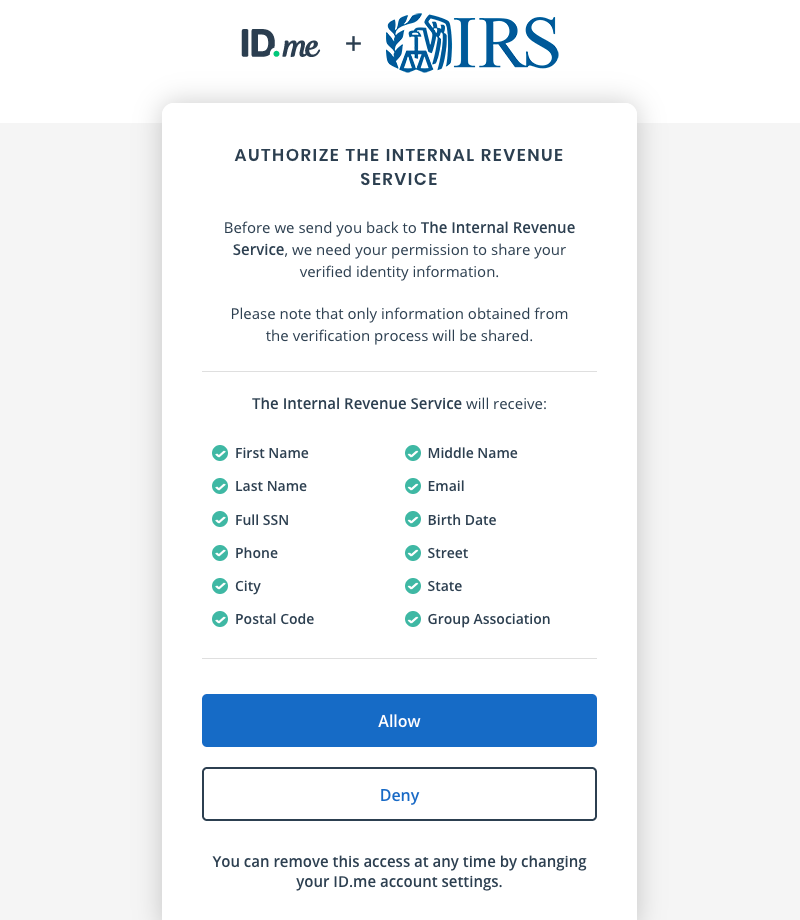
I was somewhat concerned that my ID verification might fail because I have a security freeze on my credit file with the three major consumer credit bureaus. But at no time during my application process did ID.me even mention the need to lift or thaw that security freeze to complete the authentication process.
The IRS previously relied upon Equifax for its identity proofing process, and even then anyone with frozen credit files had to lift the freeze to make it through the IRS’s legacy authentication system. For several years, the result of that reliance was that ID thieves massively abused the IRS’s own website to impersonate taxpayers, view their confidential tax records, and ultimately obtain fraudulent tax refunds in their names.
The IRS canceled its “taxpayer identity” contract with Equifax in October 2017, after the credit bureau disclosed that a failure to patch a four-month-old zero-day security flaw led to the theft of Social Security numbers and personal and financial information on 148 million Americans.
Perhaps in light of that 2017 megabreach, many readers will be rightfully concerned about being forced to provide so much sensitive information to a relatively unknown private company. KrebsOnSecurity spoke with ID.me founder and CEO Blake Hall in last year’s story, How $100 Million in Jobless Claims Went to Inmates. I asked Hall what ID.me does to secure all this sensitive information it collects, which would no doubt serve as an enticing target for hackers and identity thieves.
Hall said ID.me is certified against the NIST 800-63-3 digital identity guidelines, employs multiple layers of security, and fully segregates static consumer data tied to a validated identity from a token used to represent that identity.
“We take a defense-in-depth approach, with partitioned networks, and use very sophisticated encryption scheme so that when and if there is a breach, this stuff is firewalled,” Hall said. “You’d have to compromise the tokens at scale and not just the database. We encrypt all that stuff down to the file level with keys that rotate and expire every 24 hours. And once we’ve verified you we don’t need that data about you on an ongoing basis.”
ID.me’s privacy policy states that if you sign up for ID.me “in connection with legal identity verification or a government agency we will not use your verification information for any type of marketing or promotional purposes.”
Signing up at ID.me requires users to approve a biometric data policy that states the company will not sell, lease, or trade your biometric data to any third parties or seek to derive any profit from that information. ID.me says users can delete their biometric data at any time, but there was no apparent option to do so when I logged straight into my new account at ID.me.
When I asked the support technician who conducted the video interview to remove my biometric data, he sent me a link to a process for deleting one’s ID.me account. So, it seems that removing one’s data from ID.me post-verification equals deleting one’s account, and potentially having to re-register at some point in the future.
Over the years, I’ve tried to stress the importance of creating accounts online tied to your various identity, financial and communications services before identity thieves do it for you. But all of those places where you should “Plant Your Flag” conduct identity verification in an automated fashion, using entirely static data points about consumers that have been breached many times over (SSNs, DoBs, etc).
Love it or hate it, ID.me is likely to become one of those places where Americans need to plant their flag and mark their territory, if for no other reason than it will probably be needed at some point to manage your relationship with the federal government and/or your state. And given the potential time investment needed to successfully create an ID.me account, it might be a good idea to do that before you’re forced to do so at the last minute (such as waiting until the eleventh hour to pay your quarterly or annual estimated taxes).
If you’ve visited the sign-in page at the U.S. Social Security Administration (SSA) lately, you’ll notice that on or around Sept. 18, 2021 the agency stopped allowing new accounts to be created with only a username and password. Anyone seeking to create an account at the SSA is now steered toward either ID.me or Login.gov, a single sign-on solution for U.S. government websites.

 After entering an email address and picking a password, you are prompted to confirm your email address by clicking a link sent to that address. After confirmation, ID.me prompts users to choose a multi-factor authentication (MFA) option.
After entering an email address and picking a password, you are prompted to confirm your email address by clicking a link sent to that address. After confirmation, ID.me prompts users to choose a multi-factor authentication (MFA) option.






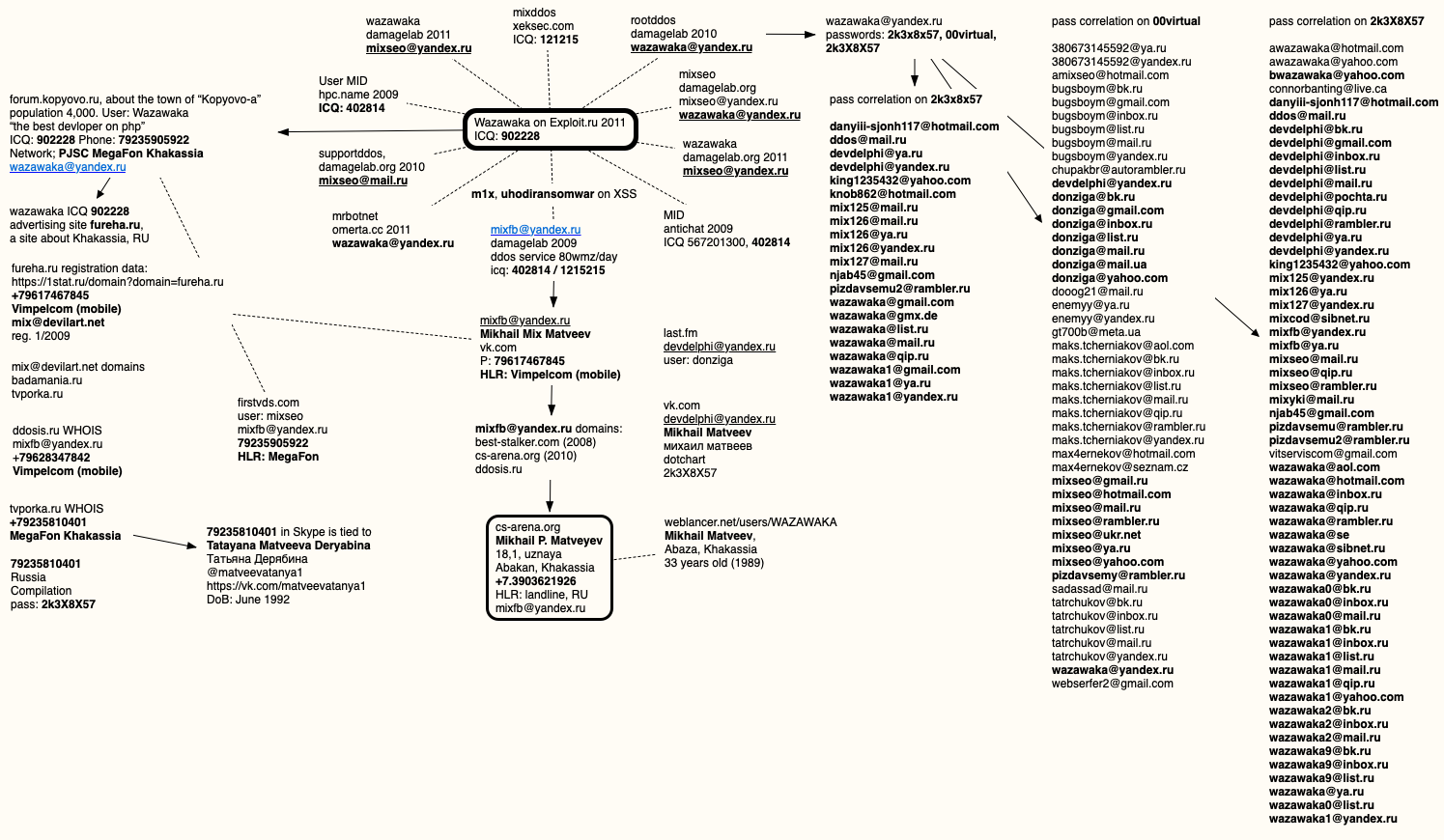

 As for the servers that were seized, they should’ve hosted their admin panels in Russia to avoid getting their servers seized by INTERPOL, the FBI, or whatever.”
As for the servers that were seized, they should’ve hosted their admin panels in Russia to avoid getting their servers seized by INTERPOL, the FBI, or whatever.”