Glut of Fake LinkedIn Profiles Pits HR Against the Bots
mercredi 5 octobre 2022 à 23:20A recent proliferation of phony executive profiles on LinkedIn is creating something of an identity crisis for the business networking site, and for companies that rely on it to hire and screen prospective employees. The fabricated LinkedIn identities — which pair AI-generated profile photos with text lifted from legitimate accounts — are creating major headaches for corporate HR departments and for those managing invite-only LinkedIn groups.

Some of the fake profiles flagged by the co-administrator of a popular sustainability group on LinkedIn.
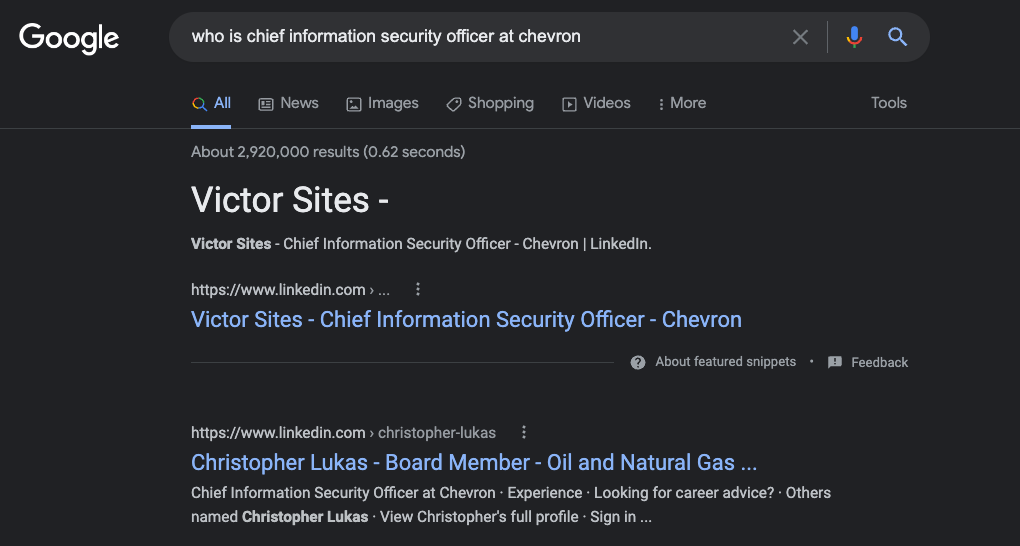
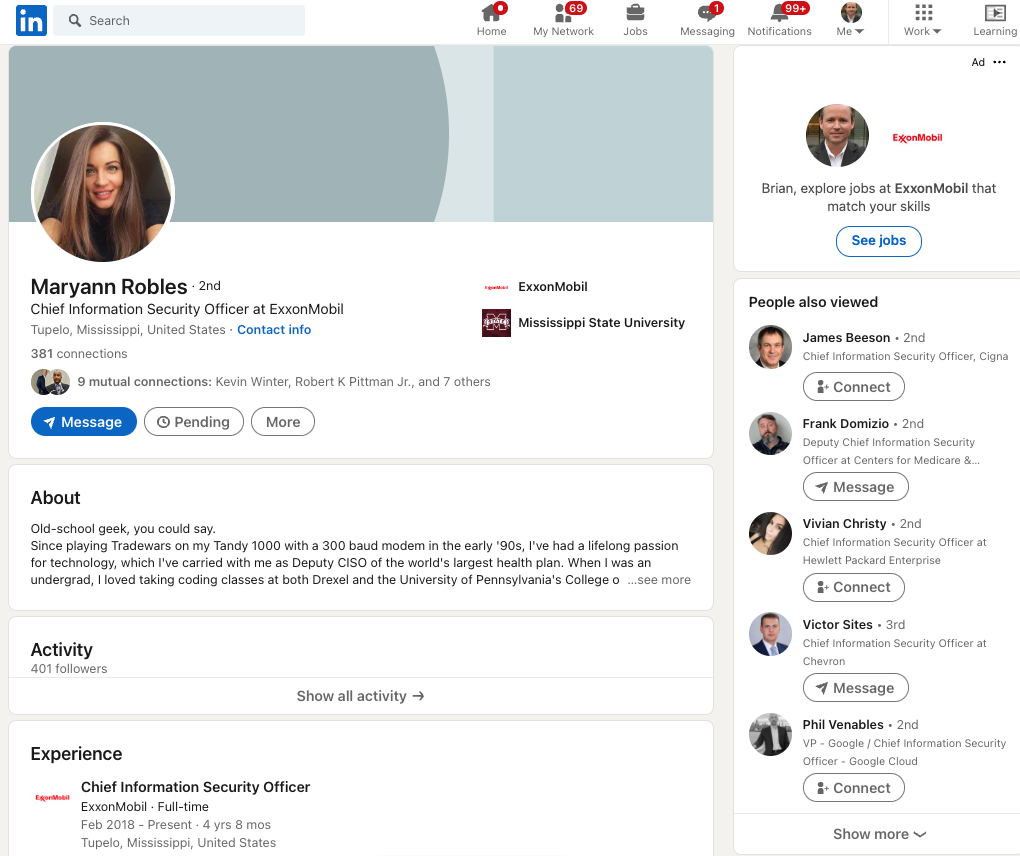
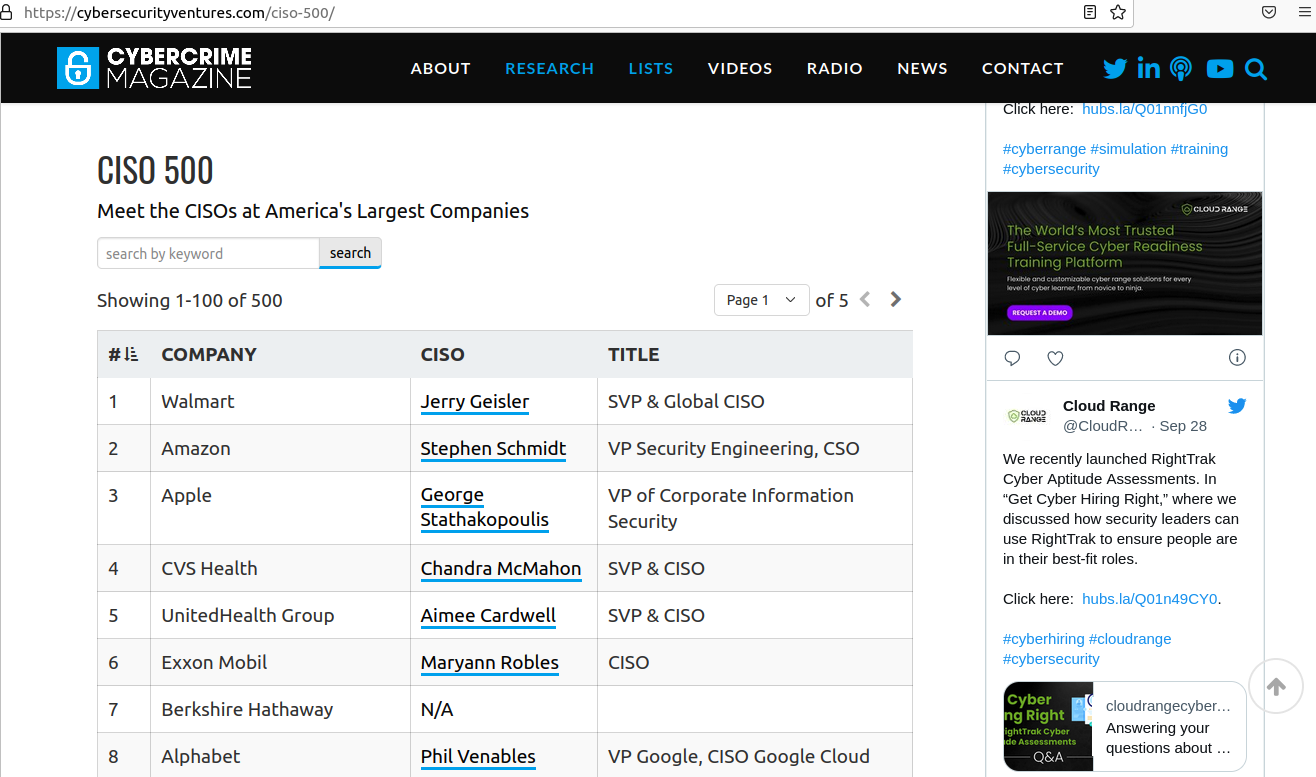
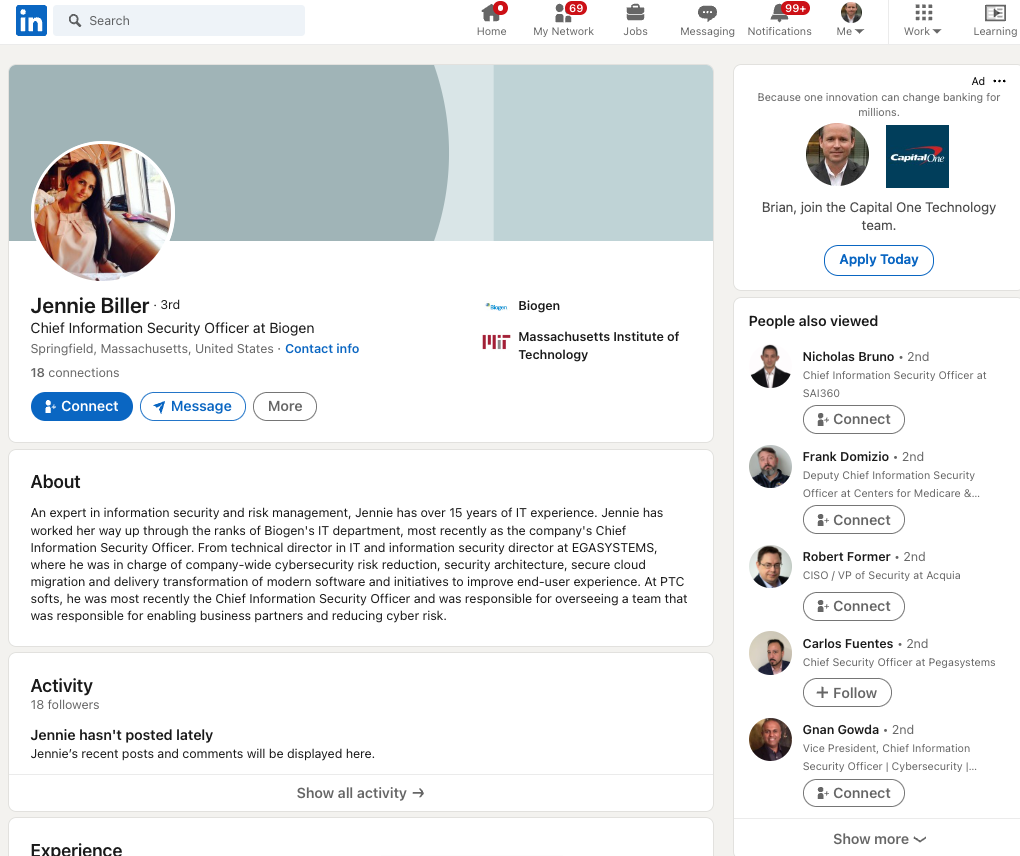
Last week, KrebsOnSecurity examined a flood of inauthentic LinkedIn profiles all claiming Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) roles at various Fortune 500 companies, including Biogen, Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Hewlett Packard.
Since then, the response from LinkedIn users and readers has made clear that these phony profiles are showing up en masse for virtually all executive roles — but particularly for jobs and industries that are adjacent to recent global events and news trends.
Hamish Taylor runs the Sustainability Professionals group on LinkedIn, which has more than 300,000 members. Together with the group’s co-owner, Taylor said they’ve blocked more than 12,700 suspected fake profiles so far this year, including dozens of recent accounts that Taylor describes as “cynical attempts to exploit Humanitarian Relief and Crisis Relief experts.”
“We receive over 500 fake profile requests to join on a weekly basis,” Taylor said. “It’s hit like hell since about January of this year. Prior to that we did not get the swarms of fakes that we now experience.”

The opening slide for a plea by Taylor’s group to LinkedIn.
Taylor recently posted an entry on LinkedIn titled, “The Fake ID Crisis on LinkedIn,” which lampooned the “60 Least Wanted ‘Crisis Relief Experts’ — fake profiles that claimed to be experts in disaster recovery efforts in the wake of recent hurricanes. The images above and below show just one such swarm of profiles the group flagged as inauthentic. Virtually all of these profiles were removed from LinkedIn after KrebsOnSecurity tweeted about them last week.

Another “swarm” of LinkedIn bot accounts flagged by Taylor’s group.
Mark Miller is the owner of the DevOps group on LinkedIn, and says he deals with fake profiles on a daily basis — often hundreds per day. What Taylor called “swarms” of fake accounts Miller described instead as “waves” of incoming requests from phony accounts.
“When a bot tries to infiltrate the group, it does so in waves,” Miller said. “We’ll see 20-30 requests come in with the same type of information in the profiles.”
After screenshotting the waves of suspected fake profile requests, Miller started sending the images to LinkedIn’s abuse teams, which told him they would review his request but that he may never be notified of any action taken.
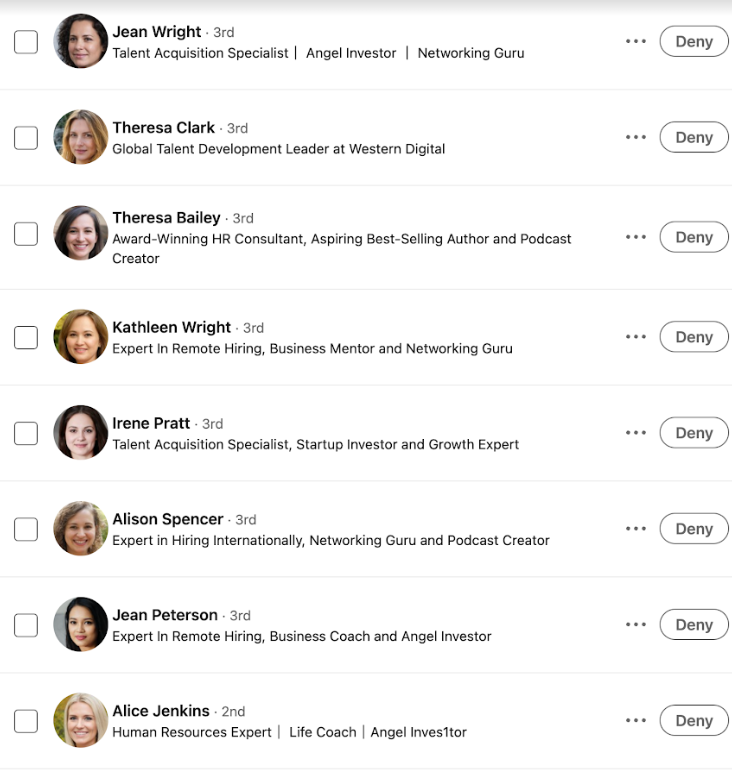
Some of the bot profiles identified by Mark Miller that were seeking access to his DevOps LinkedIn group. Miller said these profiles are all listed in the order they appeared.
Miller said that after months of complaining and sharing fake profile information with LinkedIn, the social media network appeared to do something which caused the volume of group membership requests from phony accounts to drop precipitously.
“I wrote our LinkedIn rep and said we were considering closing the group down the bots were so bad,” Miller said. “I said, ‘You guys should be doing something on the backend to block this.”
Jason Lathrop is vice president of technology and operations at ISOutsource, a Seattle-based consulting firm with roughly 100 employees. Like Miller, Lathrop’s experience in fighting bot profiles on LinkedIn suggests the social networking giant will eventually respond to complaints about inauthentic accounts. That is, if affected users complain loudly enough (posting about it publicly on LinkedIn seems to help).
Lathrop said that about two months ago his employer noticed waves of new followers, and identified more than 3,000 followers that all shared various elements, such as profile photos or text descriptions.
“Then I noticed that they all claim to work for us at some random title within the organization,” Lathrop said in an interview with KrebsOnSecurity. “When we complained to LinkedIn, they’d tell us these profiles didn’t violate their community guidelines. But like heck they don’t! These people don’t exist, and they’re claiming they work for us!”
Lathrop said that after his company’s third complaint, a LinkedIn representative responded by asking ISOutsource to send a spreadsheet listing every legitimate employee in the company, and their corresponding profile links.
Not long after that, the phony profiles that were not on the company’s list were deleted from LinkedIn. Lathrop said he’s still not sure how they’re going to handle getting new employees allowed into their company on LinkedIn going forward.
It remains unclear why LinkedIn has been flooded with so many fake profiles lately, or how the phony profile photos are sourced. Random testing of the profile photos shows they resemble but do not match other photos posted online. Several readers pointed out one likely source — the website thispersondoesnotexist.com, which makes using artificial intelligence to create unique headshots a point-and-click exercise.
Cybersecurity firm Mandiant (recently acquired by Google) told Bloomberg that hackers working for the North Korean government have been copying resumes and profiles from leading job listing platforms LinkedIn and Indeed, as part of an elaborate scheme to land jobs at cryptocurrency firms.
Fake profiles also may be tied to so-called “pig butchering” scams, wherein people are lured by flirtatious strangers online into investing in cryptocurrency trading platforms that eventually seize any funds when victims try to cash out.
In addition, identity thieves have been known to masquerade on LinkedIn as job recruiters, collecting personal and financial information from people who fall for employment scams.
But the Sustainability Group administrator Taylor said the bots he’s tracked strangely don’t respond to messages, nor do they appear to try to post content.
“Clearly they are not monitored,” Taylor assessed. “Or they’re just created and then left to fester.”
This experience was shared by the DevOp group admin Miller, who said he’s also tried baiting the phony profiles with messages referencing their fakeness. Miller says he’s worried someone is creating a massive social network of bots for some future attack in which the automated accounts may be used to amplify false information online, or at least muddle the truth.
“It’s almost like someone is setting up a huge bot network so that when there’s a big message that needs to go out they can just mass post with all these fake profiles,” Miller said.
In last week’s story on this topic, I suggested LinkedIn could take one simple step that would make it far easier for people to make informed decisions about whether to trust a given profile: Add a “created on” date for every profile. Twitter does this, and it’s enormously helpful for filtering out a great deal of noise and unwanted communications.
Many of our readers on Twitter said LinkedIn needs to give employers more tools — perhaps some kind of application programming interface (API) — that would allow them to quickly remove profiles that falsely claim to be employed at their organizations.
Another reader suggested LinkedIn also could experiment with offering something akin to Twitter’s verified mark to users who chose to validate that they can respond to email at the domain associated with their stated current employer.
In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, LinkedIn said it was considering the domain verification idea.
“This is an ongoing challenge and we’re constantly improving our systems to stop fakes before they come online,” LinkedIn said in a written statement. “We do stop the vast majority of fraudulent activity we detect in our community – around 96% of fake accounts and around 99.1% of spam and scams. We’re also exploring new ways to protect our members such as expanding email domain verification. Our community is all about authentic people having meaningful conversations and to always increase the legitimacy and quality of our community.”
In a story published Wednesday, Bloomberg noted that LinkedIn has largely so far avoided the scandals about bots that have plagued networks like Facebook and Twitter. But that shine is starting to come off, as more users are forced to waste more of their time fighting off inauthentic accounts.
“What’s clear is that LinkedIn’s cachet as being the social network for serious professionals makes it the perfect platform for lulling members into a false sense of security,” Bloomberg’s Tim Cuplan wrote. “Exacerbating the security risk is the vast amount of data that LinkedIn collates and publishes, and which underpins its whole business model but which lacks any robust verification mechanisms.”