Why Malware Crypting Services Deserve More Scrutiny
mercredi 21 juin 2023 à 20:39
If you operate a cybercrime business that relies on disseminating malicious software, you probably also spend a good deal of time trying to disguise or “crypt” your malware so that it appears benign to antivirus and security products. In fact, the process of “crypting” malware is sufficiently complex and time-consuming that most serious cybercrooks will outsource this critical function to a handful of trusted third parties. This story explores the history and identity behind Cryptor[.]biz, a long-running crypting service that is trusted by some of the biggest names in cybercrime.
Virtually all malware that is deployed for use in data stealing at some point needs to be crypted. This highly technical, laborious process involves iteratively altering the appearance and behavior of a malicious file until it no longer sets off alarm bells when scanned by different antivirus tools.
Experienced malware purveyors understand that if they’re not continuously crypting their malware before sending it out, then a lot more of whatever digital disease they are trying to spread is going to get flagged by security tools. In short, if you are running a cybercrime enterprise and you’re not equipped to handle this crypting process yourself, you probably need to pay someone else to do it for you.
Thanks to the high demand for reliable crypting services, there are countless cybercriminals who’ve hung out their shingles as crypting service providers. However, most of these people do not appear to be very good at what they do, because most are soon out of business.
One standout is Cryptor[.]biz. This service is actually recommended by the purveyors of the RedLine information stealer malware, which is a popular and powerful malware kit that specializes in stealing victim data and is often used to lay the groundwork for ransomware attacks. Cryptor[.]biz also has been recommended to customers of the Predator information stealer malware family (via the malware’s Telegram support channels).
WHO RUNS CRYPTOR[.]BIZ?
As good as Cryptor[.]biz may be at obfuscating malware, its proprietor does not appear to have done a great job covering his own tracks. The registration records for the website Cryptor[.]biz are hidden behind privacy protection services, but the site’s homepage says potential customers should register by visiting the domain crypt[.]guru, or by sending a Jabber instant message to the address “masscrypt@exploit.im.”
Crypt[.]guru’s registration records also are hidden, yet passive domain name system (DNS) records for both cryptor[.]biz and crypt[.]guru show that in 2018 the domains were forwarding incoming email to the address obelisk57@gmail.com.
Cyber intelligence firm Intel 471 reports that obelisk57@gmail.com was used to register an account on the forum Blacksoftware under the nickname “Kerens.” Meanwhile, the Jabber address masscrypt@exploit.im has been associated with the user Kerens on the Russian hacking forum Exploit from 2011 to the present day.

The login page for Cryptor dot biz contains several clues about who runs the service.
The very first post by Kerens on Exploit in 2011 was a negative review of a popular crypting service that predated Cryptor[.]biz called VIP Crypt, which Kerens accused of being “shitty” and unreliable. But Intel 471 finds that after his critical review of VIP Crypt, Kerens did not post publicly on Exploit again for another four years until October 2016, when they suddenly began advertising Cryptor[.]biz.
Intel 471 found that Kerens used the email address pepyak@gmail.com, which also was used to register Kerens accounts on the Russian language hacking forums Verified and Damagelab.
Ironically, Verified has itself been hacked multiple times over the years, with its private messages and user registration details leaked online. Those records indicate the user Kerens registered on Verified in March 2009 from an Internet address in Novosibirsk, a city in the southern Siberian region of Russia.
In 2010, someone with the username Pepyak on the Russian language affiliate forum GoFuckBiz[.]com shared that they typically split their time during the year between living in Siberia (during the milder months) and Thailand (when Novosibirsk is typically -15 °C/°5F).
For example, in one conversation about the best car to buy for navigating shoddy roads, Pepyak declared, “We have shitty roads in Siberia.” In January 2010, Pepyak asked the GoFuckBiz community where one might find a good USB-based modem in Phuket, Thailand.
DomainTools.com says the email address pepyak@gmail.com was used to register 28 domain names over the years, including a now-defunct Russian automobile sales website called “autodoska[.]biz.” DomainTools shows this website was registered in 2008 to a Yuri Churnov from Sevastpol, Crimea (prior to Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014, the peninsula was part of Ukraine).
The WHOIS records for autodoska[.]biz were changed in 2010 to Sergey Purtov (pepyak@gmail.com) from Yurga, a town in Russia’s Kemerovo Oblast, which is a relatively populous area in Western Siberia that is adjacent to Novosibirsk.
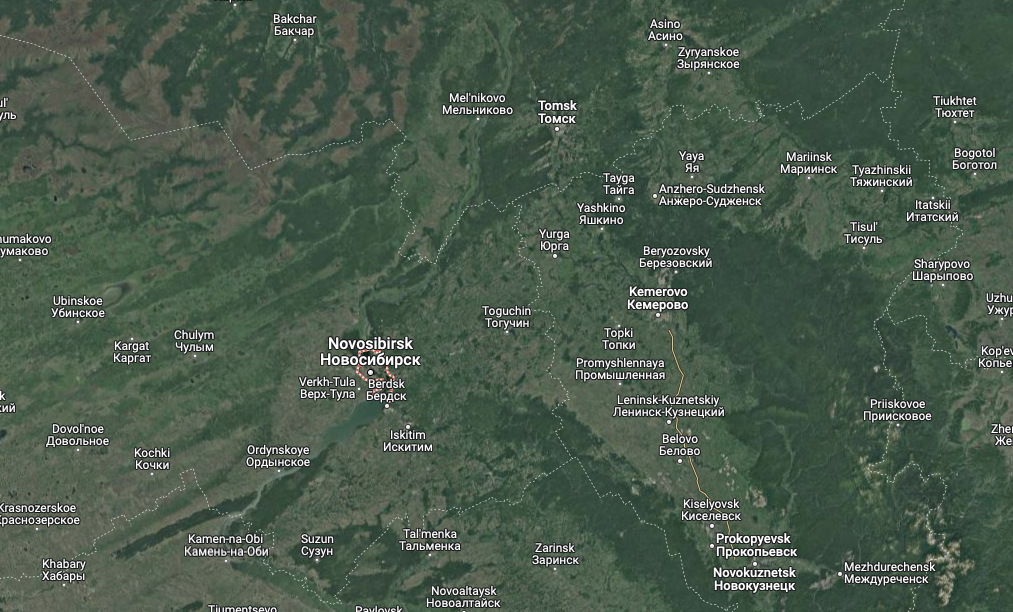
A satellite view of the region including Novosibirsk, Yurga and Kemerovo Oblast. Image: Google Maps.
Many of the 28 domains registered to pepyak@gmail.com have another email address in their registration records: unforgiven57@mail.ru. According to DomainTools, the Unforgiven email address was used to register roughly a dozen domains, including three that were originally registered to Keren’s email address — pepyak@gmail.com (e.g., antivirusxp09[.]com).
One of the domains registered in 2006 to the address unforgiven57@mail.ru was thelib[.]ru, which for many years was a place to download pirated e-books. DomainTools says thelib[.]ru was originally registered to a Sergey U Purtov.
Most of the two-dozen domains registered to pepyak@gmail.com shared a server at one point with a small number of other domains, including mobile-soft[.]su, which was registered to the email address spurtov@gmail.com.
CDEK, an express delivery company based in Novosibirsk, was apparently hacked at some point because cyber intelligence firm Constella Intelligence found that its database shows the email address spurtov@gmail.com was assigned to a Sergey Yurievich Purtov (Сергей Юрьевич Пуртов).
DomainTools says the same phone number in the registration records for autodoska[.]biz (+7.9235059268) was used to secure two other domains — bile[.]ru and thelibrary[.]ru, both of which were registered to a Sergey Y Purtov.
 A search on the phone number 79235059268 in Skype reveals these digits belong to a “Sergey” from Novosibirsk with the now-familiar username — Pepyak.
A search on the phone number 79235059268 in Skype reveals these digits belong to a “Sergey” from Novosibirsk with the now-familiar username — Pepyak.
Bringing things full circle, Constella Intelligence shows that various online accounts tied to the email address unforgiven57@mail.ru frequently relied on the somewhat unique password, “plk139t51z.” Constella says that same password was used for just a handful of other email addresses, including gumboldt@gmail.com.
Hacked customer records from CDEK show gumboldt@gmail.com was tied to a customer named Sergey Yurievich Purtov. DomainTools found that virtually all of the 15 domain names registered to gumboldt@gmail.com (including the aforementioned mobile-soft[.]su) were at one point registered to spurtov@gmail.com.
Intel 471 reports that gumboldt@gmail.com was used in 2009 to register a user by the nickname “Kolumb” on the Russian hacking forum Antichat. From Kolumb’s posts on Antichat, it seems this user was mostly interested in buying access to compromised computers inside of Russia.
Then in December 2009, Kolumb said they were in desperate need of a reliable crypting service or full-time cryptor.
“We need a person who will crypt software every day, sometimes even a couple of times a day,” Kolumb wrote on Antichat.
Mr. Purtov did not respond to requests for comment sent to any of the email addresses referenced in this report. Mail.ru responded that the email address spurtov@mail.ru is no longer active.
ANALYSIS
As KrebsOnSecurity opined on Mastodon earlier this week, it makes a lot of sense for cybersecurity researchers and law enforcement alike to focus attention on the top players in the crypting space — for several reasons. Most critically, the cybercriminals offering time-tested crypting services also tend to be among the most experienced and connected malicious coders on the planet.
Think of it this way: By definition, a crypting service scans and examines all types of malware before those new nasties are first set loose in the wild. This fact alone should make these criminal enterprises a primary target of cybersecurity firms looking to gain more timely intelligence about new malware.
Also, a review of countless posts and private messages from Pepyak and other crypting providers shows that a successful crypting service will have direct and frequent contact with some of the world’s most advanced malware authors.
In short, infiltrating or disrupting a trusted crypting service can be an excellent way to slow down or even sideline a large number of cybercrime operations all at once.
Further reading on the crypting industry:
This Service Helps Malware Authors Fix Flaws in Their Code
Antivirus is Dead: Long Live Antivirus!